Introduction: The Dawn of AI-Powered E-Commerce Development
Picture this: You’re building a complex Magento 2 integration—maybe a custom checkout flow, an advanced product import system, or a sophisticated order management dashboard. Traditionally, this means hours of browsing documentation, cross-referencing REST and GraphQL APIs, and constantly switching between browser tabs and your IDE. But what if an AI agent could access the entire Magento documentation instantly, understand your requirements, and generate production-ready code in minutes?
Welcome to the world of agentic development for Magento 2, where AI agents augmented with Model Context Protocol (MCP) servers transform how we build e-commerce applications. Today, I’m excited to introduce two powerful open-source MCP servers that bring the complete Magento 2 REST API and GraphQL documentation directly to AI agents like Claude, enabling unprecedented development speed and accuracy.
These aren’t just documentation search tools—they’re intelligent bridges between AI agents and Magento’s vast API ecosystem, covering 594 REST endpoints, 350+ GraphQL documentation pages, and nearly 1,000 working code examples. Whether you’re implementing authentication flows, building product catalogs, or creating complex B2B integrations, these MCP servers provide instant, structured access to everything an AI agent needs to generate correct, production-ready code.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore how these MCP servers work, why they matter for Magento 2 AI development, and how you can start using them today to build intelligent applications faster than ever before.
Understanding Model Context Protocol for AI Development
What is Model Context Protocol?
Model Context Protocol (MCP), developed by Anthropic, is a standardized communication protocol that enables AI agents to interact with external tools and data sources. Think of it as USB for AI—a universal interface that lets AI models “plug into” different capabilities without custom integrations for each tool.
At its core, MCP creates a client-server architecture where:
- MCP Clients are AI applications (like Claude Desktop, custom AI agents, or development tools)
- MCP Servers are specialized tools that expose specific capabilities (documentation search, database access, API integrations)
- Communication happens over STDIO (standard input/output), making it simple, fast, and language-agnostic
Why MCP Matters for Documentation Access
Traditional approaches to giving AI agents documentation access have significant limitations:
Web Scraping: Slow (30-60 seconds startup), requires network access, parsing HTML is error-prone, and results are unstructured.
Direct API Calls: Limited by rate limits, network latency, and often lacks comprehensive documentation coverage.
Manual Copy-Paste: Doesn’t scale, introduces human error, and can’t keep up with AI agent speed.
MCP solves these problems by providing:
✅ Offline Operation – No network dependency, works anywhere
✅ Lightning-Fast Search – Millisecond response times with FTS5 indexes
✅ Structured Data – Properly formatted schemas, parameters, and responses
✅ Context-Aware – AI agents can explore documentation relationships
✅ Always Current – Local documentation ensures consistency
For Magento 2 development specifically, MCP enables AI agents to:
- Search 594 REST endpoints in <100ms
- Find GraphQL queries and mutations instantly (5.5ms average)
- Access 963 code examples with surrounding context
- Explore 13 step-by-step tutorials for complex workflows
- Understand data schemas and type definitions completely
This transforms AI from “helpful assistant with occasional hallucinations” to “expert developer with perfect memory of every Magento API.”
Two Powerful MCP Servers for Magento 2 Development
The Magento 2 ecosystem now has two complementary MCP servers, each optimized for different aspects of API development:
Magento REST API MCP Server
GitHub Repository: github.com/florinel-chis/magento-api-mcp
This server provides complete access to Magento 2’s REST API through OpenAPI 3.0 specifications. It parses the official swagger.json file (70,000+ lines) and creates an intelligent, searchable index of every REST endpoint, parameter, schema, and response code.
Key Capabilities:
- 594 REST Endpoints – Complete coverage of Magento REST API
- 497 Data Schemas – Full OpenAPI schema definitions
- 825+ Parameters – Every path, query, and header parameter documented
- 5 Specialized Tools – Search, browse, and explore the REST API
- OpenAPI Native – Leverages structured OpenAPI format for accuracy
Best For: REST API integrations, CRUD operations, traditional API clients, and scenarios requiring precise schema definitions.
Magento GraphQL Documentation MCP Server
GitHub Repository: github.com/florinel-chis/magento-graphql-docs-mcp
This server provides access to Magento 2’s narrative GraphQL documentation from Adobe’s official docs. Unlike raw API specs, this includes tutorials, guides, explanations, and 963 working code examples.
Key Capabilities:
- 350 Documentation Pages – Comprehensive GraphQL coverage
- 963 Code Examples – GraphQL (537), JSON (363), PHP (18), JavaScript, Bash
- 51 GraphQL Elements – Queries, mutations, types, and interfaces
- 13 Complete Tutorials – Including 12-step checkout workflow
- 8 Specialized Tools – Search, explore, learn, and implement
- Context-Rich – Includes explanations, best practices, and use cases
Best For: GraphQL development, learning complex workflows, finding working examples, and understanding “why” not just “what.”
Side-by-Side Comparison
| Feature | REST API MCP | GraphQL Docs MCP |
|---|---|---|
| Data Source | OpenAPI 3.0 (swagger.json) | Markdown files (350+) |
| Content Type | Structured API specs | Narrative docs + tutorials |
| Endpoints/Docs | 594 REST endpoints | 350 documents |
| Code Examples | OpenAPI examples | 963 code blocks |
| Schema Info | 497 data models | 51 GraphQL elements |
| Startup Time | 3-5 seconds | 0.87-5 seconds |
| Search Speed | <100ms | 5.5ms average (18x faster) |
| MCP Tools | 5 tools | 8 tools |
| Offline | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes |
| Database | SQLite + FTS5 | SQLite + FTS5 |
| Best For | REST integration | GraphQL + learning |
| Tutorial Support | ❌ No | ✅ 13 tutorials |
| Working Examples | Limited | 963 examples |
The Power of Both Together:
Many Magento 2 projects use both REST and GraphQL APIs. With both MCP servers running simultaneously, AI agents can:
- Compare REST vs GraphQL approaches for the same functionality
- Use REST for simple CRUD, GraphQL for complex queries
- Learn from GraphQL tutorials, implement with either API
- Access the complete Magento API ecosystem
Magento REST API MCP Server: Complete API Reference at Your Fingertips
Architecture & Capabilities
The REST API MCP Server is built on a three-layer architecture optimized for speed and accuracy:
1. Parser Layer
Uses Pydantic models to parse the 70,000-line OpenAPI 3.0 swagger.json file, extracting endpoints, parameters, request bodies, response schemas, and metadata. Every element is validated and type-checked during parsing.
2. Ingestion Layer
Creates a SQLite database with FTS5 (Full-Text Search 5) indexes on endpoint paths, descriptions, tags, and parameters. File modification time tracking ensures the database only rebuilds when swagger.json changes—subsequent startups take just 2-3 seconds.
3. Server Layer
FastMCP framework exposes 5 specialized tools over STDIO, formatting responses as structured markdown with tables, code blocks, and expandable schemas.
The 5 MCP Tools in Action
1. search_endpoints – Find REST Endpoints Instantly
Search all 594 endpoints using keywords, with optional filters by HTTP method or category tag.
Example Query:
search_endpoints(
queries=["cart operations"],
filter_by_method="GET",
filter_by_tag="carts"
)
Returns:
### GET /V1/carts/mine
**Category:** carts/mine
**Summary:** Return information for the cart for a specified customer
### GET /V1/carts/{cartId}
**Category:** carts
**Summary:** Return information for a specified cart
Use Case: An AI agent building a cart display component can instantly find all GET endpoints related to carts, understand their purposes, and choose the right one.
2. get_endpoint_details – Complete Endpoint Documentation
Retrieve full documentation for any endpoint, including parameters, request body schemas, and response definitions.
Example:
get_endpoint_details(
path="/V1/products",
method="POST"
)
Returns:
- Complete parameter list with types and descriptions
- Request body schema with all required/optional fields
- Response schema for each status code (200, 400, 401, etc.)
- Examples and references
Use Case: When generating product import code, the AI agent gets the exact schema structure needed, including field types, validation rules, and response handling.
3. list_tags – Browse API by Category
Get a hierarchical view of all endpoint categories with document counts.
Returns:
## carts (24 endpoints)
- carts/mine: 12 endpoints
- carts/guest: 8 endpoints
## customers (36 endpoints)
- customers/me: 14 endpoints
- customers/addresses: 10 endpoints
Use Case: Explore the API structure to understand what’s available before diving into specific endpoints.
4. search_schemas – Find Data Models
Search through 497 schema definitions to find the right data model.
Example:
search_schemas(query="customer address")
Returns matching schemas:
customer-data-address-interfacecustomer-data-region-interfacedirectory-data-region-information-interface
5. get_schema – View Complete Schema Definitions
Retrieve full schema details with all properties, types, and descriptions.
Example:
get_schema(name="catalog-data-product-interface")
Returns: JSON object with every product property, its type, whether it’s required, and its description—everything needed to construct valid API requests.
Real-World Use Case: Building a Product Import Tool
Let’s see how an AI agent uses the REST API MCP Server to build a production-ready product import tool:
Step 1: Discovery
Agent: search_endpoints(queries=["product import", "create product"])
→ Finds POST /V1/products endpoint
Step 2: Understanding
Agent: get_endpoint_details(path="/V1/products", method="POST")
→ Gets request schema: catalog-data-product-interface
→ Understands required fields: sku, name, price, attribute_set_id, status
Step 3: Schema Exploration
Agent: get_schema(name="catalog-data-product-interface")
→ Sees all 50+ product properties
→ Understands nested structures (custom_attributes, extension_attributes)
→ Identifies optional vs required fields
Step 4: Code Generation
The AI agent generates:
import requests
import json
def import_product(product_data, api_token, base_url):
"""
Import a product to Magento 2 via REST API
Schema: catalog-data-product-interface
Endpoint: POST /V1/products
"""
endpoint = f"{base_url}/rest/V1/products"
headers = {
"Authorization": f"Bearer {api_token}",
"Content-Type": "application/json"
}
payload = {
"product": {
"sku": product_data["sku"],
"name": product_data["name"],
"price": product_data["price"],
"attribute_set_id": product_data.get("attribute_set_id", 4),
"status": product_data.get("status", 1),
"visibility": product_data.get("visibility", 4),
"type_id": product_data.get("type_id", "simple"),
"weight": product_data.get("weight", 1.0),
# ... all other required/optional fields
}
}
response = requests.post(endpoint, json=payload, headers=headers)
if response.status_code == 200:
return {"success": True, "product": response.json()}
else:
return {
"success": False,
"error": response.json(),
"status_code": response.status_code
}
Total Time: Under 30 seconds from “build me a product import tool” to production-ready code with error handling.
Installation & Setup
# Clone the repository
git clone https://github.com/florinel-chis/magento-api-mcp
cd magento-api-mcp
# Install dependencies
pip install -e .
# Run the server
magento-api-mcp
# Verify it's working
python3 tests/verify_server.py
Configure with Claude Desktop:
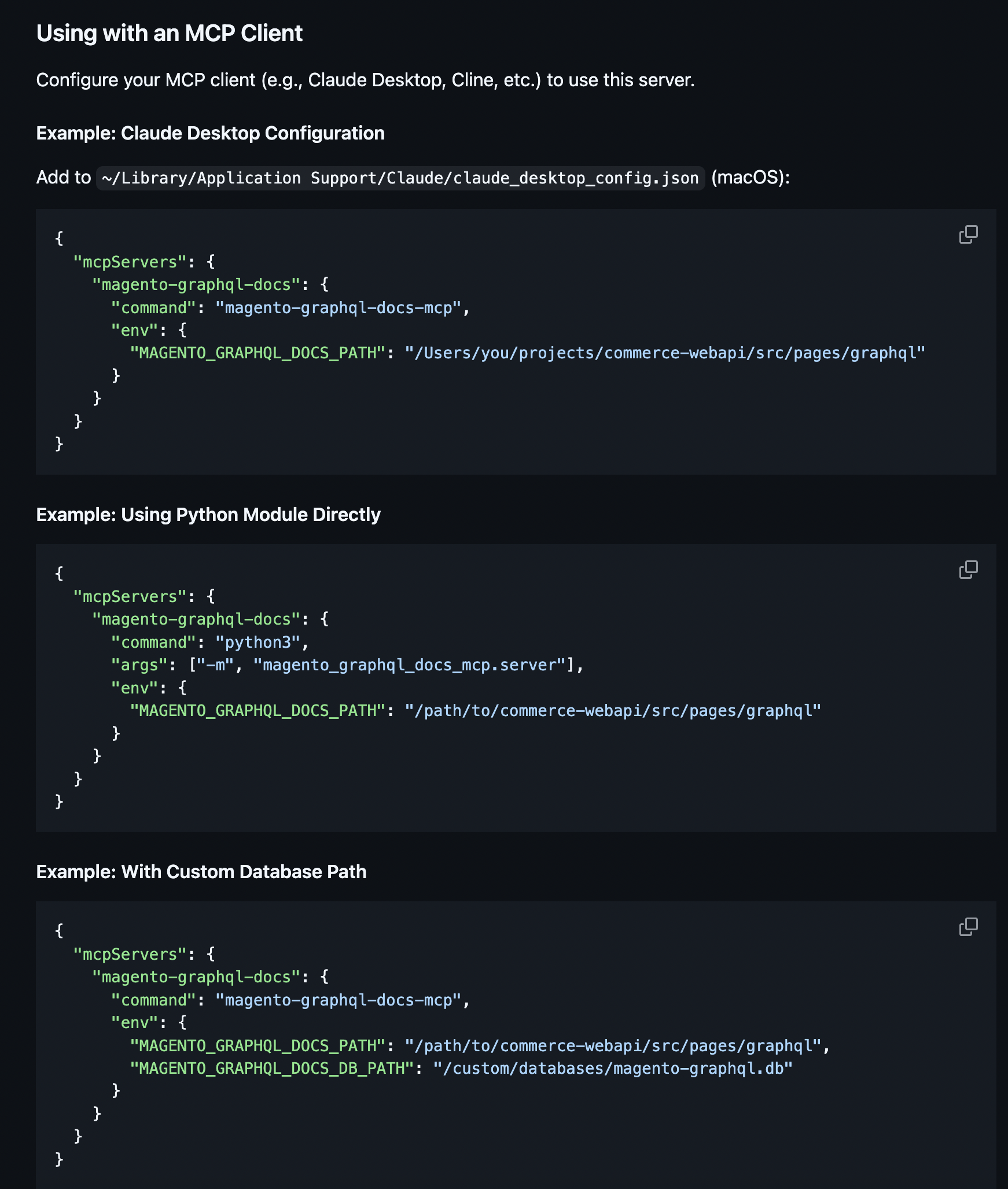
Edit ~/Library/Application Support/Claude/claude_desktop_config.json (macOS):
{
"mcpServers": {
"magento-api": {
"command": "magento-api-mcp"
}
}
}
Restart Claude Desktop, and the REST API tools are immediately available.
Magento GraphQL Documentation MCP Server: Learning and Implementation Combined
Architecture & Capabilities
While the REST API server focuses on structured specifications, the GraphQL Documentation MCP Server brings narrative documentation, tutorials, and working examples to AI agents.
Three-Layer Architecture:
1. Parser Layer
Parses 350 markdown files with YAML frontmatter, extracting metadata (title, description, keywords), document structure (headers, code blocks), and GraphQL schema elements (queries, mutations, types, interfaces). Uses regex-based GraphQL element detection to identify 51 schema elements across the documentation.
2. Ingestion Layer
Creates a sophisticated SQLite database with:
- documents table: 350 pages with FTS5 index on combined searchable text
- code_blocks table: 963 examples with language tags and context
- graphql_elements table: 51 elements with FTS5 index
- metadata table: Tracks file modification times for intelligent re-ingestion
File modification time checking means subsequent startups take just 0.87 seconds—dramatically faster than the REST API server.
3. Server Layer
Eight specialized MCP tools provide comprehensive access to documentation, tutorials, examples, and schema exploration.
The 8 MCP Tools: Complete GraphQL Coverage
1. search_documentation – Find Documentation Pages
Full-text search with sophisticated filtering by category, subcategory, and content type.
Example:
search_documentation(
queries=["checkout flow"],
category="tutorials",
content_type="tutorial"
)
Returns:
### GraphQL checkout tutorial
**Path:** tutorials/checkout/index.md
**Category:** tutorials/checkout
**Type:** tutorial
**Description:** Learn how to implement a complete checkout flow with GraphQL
Advanced Features:
- Multi-keyword queries with OR logic
- Category filtering (schema, tutorials, develop, usage)
- Content type filtering (guide, reference, tutorial, schema)
- Returns top 5 results with relevance scoring
2. get_document – Retrieve Complete Documentation
Get the full markdown content of any documentation page, including frontmatter metadata.
Returns:
- Complete YAML frontmatter (title, description, keywords)
- Category and subcategory
- Full markdown content with preserved formatting
- Related document suggestions
3. search_graphql_elements – Find Queries, Mutations, Types
Search the 51 extracted GraphQL schema elements with optional type filtering.
Example:
search_graphql_elements(
query="customer",
element_type="mutation"
)
Returns:
### `mutation` **createCustomer**
**Source:** usage/index.md
**Fields:** customer, input, firstname, lastname, email
**Parameters:** CustomerInput
4. get_element_details – Complete Element Information
Retrieve full details about any GraphQL element, including fields, parameters, source documentation, and up to 3 code examples.
Example:
get_element_details(
element_name="ProductInterface",
element_type="interface"
)
Returns:
- All fields (name, sku, price, description, etc.)
- Parameters if applicable
- Return type
- Source document reference
- Working GraphQL code examples
5. list_categories – Browse Documentation Hierarchy
Get a complete tree view of all documentation categories with document counts.
Returns:
## schema (285 documents)
- products: 32 documents
- cart: 18 documents
- customer: 24 documents
## tutorials (13 documents)
- checkout: 12 documents
## develop (8 documents)
Use Case: Understand the documentation structure before diving into specific areas.
6. get_tutorial – Sequential Tutorial Steps
Retrieve complete tutorials with all steps in order, including code examples.
Example:
get_tutorial(tutorial_name="checkout")
Returns: The complete 12-step checkout tutorial:
- Create empty cart
- Add products to cart
- Get cart details
- Set shipping address
- Set billing address
- Set shipping method
- Set payment method
- Apply coupon (optional)
- Place order
- Get order details
- Handle errors
- Complete workflow
Each step includes GraphQL queries/mutations and expected responses.
7. search_examples – Find Working Code
Search through 963 code blocks by content and language.
Example:
search_examples(
query="add to cart",
language="graphql"
)
Returns:
mutation {
addProductsToCart(
cartId: "{ CART_ID }"
cartItems: [
{
quantity: 1
sku: "24-MB01"
}
]
) {
cart {
items {
id
product {
name
sku
}
quantity
}
}
}
}
Context included: The surrounding explanation from the documentation, making examples immediately understandable.
8. get_related_documents – Discover Related Content
Find documents related to a specified page based on category and keywords.
Use Case: After reading about product queries, AI agent discovers related documentation on product filters, pagination, and sorting—enabling comprehensive implementation.
Real-World Use Case: Implementing GraphQL Checkout Flow
Let’s watch an AI agent use the GraphQL Documentation MCP Server to implement a complete checkout flow:
Step 1: Tutorial Discovery
Agent: get_tutorial(tutorial_name="checkout")
→ Receives 12-step workflow
→ Understands createEmptyCart → addProductsToCart → ... → placeOrder
Step 2: Mutation Exploration
Agent: search_graphql_elements(query="cart", element_type="mutation")
→ Finds all cart-related mutations
→ Identifies createEmptyCart, addProductsToCart, setShippingAddressesOnCart, etc.
Step 3: Working Examples
Agent: search_examples(query="addProductsToCart", language="graphql")
→ Gets actual working GraphQL query
→ Sees expected response structure
→ Understands error handling
Step 4: Related Documentation
Agent: get_related_documents(file_path="tutorials/checkout/add-product-to-cart.md")
→ Discovers cart validation documentation
→ Finds error handling guides
→ Locates payment method configuration docs
Step 5: Code Generation
The AI agent generates a complete TypeScript/JavaScript implementation:
import { ApolloClient, gql } from '@apollo/client';
interface CheckoutFlowParams {
products: Array<{ sku: string; quantity: number }>;
shippingAddress: Address;
billingAddress: Address;
shippingMethod: string;
paymentMethod: PaymentMethod;
}
class MagentoCheckout {
private client: ApolloClient;
private cartId: string | null = null;
constructor(apiUrl: string) {
this.client = new ApolloClient({ uri: apiUrl });
}
async executeCheckout(params: CheckoutFlowParams): Promise<OrderResult> {
try {
// Step 1: Create empty cart
this.cartId = await this.createCart();
// Step 2: Add products
await this.addProducts(params.products);
// Step 3: Set shipping address
await this.setShippingAddress(params.shippingAddress);
// Step 4: Set billing address
await this.setBillingAddress(params.billingAddress);
// Step 5: Set shipping method
await this.setShippingMethod(params.shippingMethod);
// Step 6: Set payment method
await this.setPaymentMethod(params.paymentMethod);
// Step 7: Place order
const orderId = await this.placeOrder();
return { success: true, orderId };
} catch (error) {
return { success: false, error: error.message };
}
}
private async createCart(): Promise<string> {
const CREATE_CART = gql`
mutation {
createEmptyCart
}
`;
const { data } = await this.client.mutate({ mutation: CREATE_CART });
return data.createEmptyCart;
}
private async addProducts(products: Array<{ sku: string; quantity: number }>): Promise<void> {
const ADD_PRODUCTS = gql`
mutation($cartId: String!, $cartItems: [CartItemInput!]!) {
addProductsToCart(cartId: $cartId, cartItems: $cartItems) {
cart {
id
items {
id
quantity
product {
sku
name
}
}
}
}
}
`;
await this.client.mutate({
mutation: ADD_PRODUCTS,
variables: {
cartId: this.cartId,
cartItems: products.map(p => ({
sku: p.sku,
quantity: p.quantity
}))
}
});
}
// ... additional methods for each checkout step
}
Total Time: From “implement checkout flow” to production-ready TypeScript class: under 2 minutes.
Unique Advantages: Narrative + Code + Tutorials
The GraphQL Documentation MCP Server’s real power comes from combining three types of content:
1. Narrative Documentation (“Why” and “How”)
- Explains concepts, not just syntax
- Provides context and use cases
- Includes best practices and recommendations
2. Working Code Examples (963 Examples)
- GraphQL queries and mutations (537)
- JSON request/response examples (363)
- PHP implementation examples (18)
- JavaScript/Bash examples
- Context surrounding each example
3. Step-by-Step Tutorials (13 Complete Tutorials)
- Checkout workflow (12 steps)
- Order creation workflows
- Customer authentication flows
- Product catalog implementation
- Payment integration guides
This combination means AI agents don’t just generate code—they generate correct, production-ready, best-practice code based on official documentation.
Installation & Setup
The GraphQL Documentation MCP Server requires access to Adobe’s official Magento documentation files:
# Step 1: Clone Adobe Commerce documentation
git clone https://github.com/AdobeDocs/commerce-webapi.git
# Step 2: Clone the MCP server
git clone https://github.com/florinel-chis/magento-graphql-docs-mcp
cd magento-graphql-docs-mcp
# Step 3: Install dependencies
pip install -e .
# Step 4: Configure documentation path
export MAGENTO_GRAPHQL_DOCS_PATH="/path/to/commerce-webapi/src/pages/graphql"
# Or create a symlink
ln -s /path/to/commerce-webapi/src/pages/graphql data
# Step 5: Run verification tests
python3 tests/verify_parser.py
python3 tests/verify_db.py
python3 tests/verify_server.py
# Step 6: Start the server
magento-graphql-docs-mcp
Configure with Claude Desktop:
{
"mcpServers": {
"magento-graphql-docs": {
"command": "magento-graphql-docs-mcp",
"env": {
"MAGENTO_GRAPHQL_DOCS_PATH": "/absolute/path/to/commerce-webapi/src/pages/graphql"
}
}
}
}
Try the Examples:
The repository includes three practical examples demonstrating all 8 tools:
cd examples
# Example 1: Product queries and catalog
python3 example_products.py
# Example 2: Customer operations and authentication
python3 example_customer.py
# Example 3: Complete cart and checkout workflow
python3 example_cart_checkout.py
# Or run all at once
bash run_all_examples.sh
Agentic Development: AI Agents Building Magento Applications
What is Agentic Development?
Agentic development represents a paradigm shift in software engineering. Instead of developers writing every line of code manually, AI agents autonomously complete development tasks through:
1. Context Awareness: Understanding requirements, constraints, and goals
2. Tool Use: Accessing external systems like MCP servers
3. Iterative Problem-Solving: Breaking complex tasks into steps
4. Decision Making: Choosing appropriate approaches and APIs
5. Code Generation: Producing production-ready implementations
With MCP servers, AI agents gain “superpowers”—instant access to comprehensive documentation, working examples, and schema definitions. They don’t hallucinate API endpoints or invent parameter names; they reference actual Magento documentation to generate correct code.
Complete Agentic Workflow: Building a Custom Checkout Flow
Let’s follow an AI agent as it builds a custom checkout flow from scratch, using both MCP servers:
Phase 1: Discovery & Planning
User Request: “Build a custom checkout flow that supports guest checkout, validates inventory, applies promotional codes, and handles multiple payment methods.”
Agent Analysis:
Agent thinks:
- Need to understand Magento checkout workflow
- Should support both REST and GraphQL (REST for admin, GraphQL for frontend)
- Requires cart creation, product validation, address handling, payment processing
- Must handle errors gracefully
Agent actions:
1. get_tutorial(tutorial_name="checkout") from GraphQL MCP
2. search_endpoints(queries=["checkout", "guest"]) from REST MCP
3. list_categories() from both servers to understand structure
Result: Agent understands the complete checkout workflow and identifies required components.
Phase 2: API Exploration
GraphQL Approach:
Agent calls:
- search_graphql_elements(query="cart", element_type="mutation")
- get_element_details(element_name="createEmptyCart")
- get_element_details(element_name="addProductsToCart")
- search_examples(query="placeOrder", language="graphql")
REST Approach:
Agent calls:
- search_endpoints(queries=["cart"], filter_by_method="POST")
- get_endpoint_details(path="/V1/guest-carts")
- get_schema(name="quote-data-cart-interface")
Result: Agent compares REST vs GraphQL approaches, decides GraphQL is better for this use case due to reduced over-fetching and cleaner mutations.
Phase 3: Schema Understanding
Data Structure Exploration:
Agent calls:
- get_element_details(element_name="CartInterface", element_type="interface")
- get_element_details(element_name="ShippingAddressInput", element_type="type")
- get_element_details(element_name="PaymentMethodInput", element_type="type")
- search_examples(query="address validation", language="json")
Result: Agent understands:
- Cart structure (items, addresses, totals, discounts)
- Required vs optional fields
- Nested object structures
- Error response formats
Phase 4: Implementation
The agent generates a complete React component with TypeScript:
import React, { useState } from 'react';
import { useMutation, useQuery } from '@apollo/client';
import {
CREATE_EMPTY_CART,
ADD_PRODUCTS_TO_CART,
SET_SHIPPING_ADDRESS,
SET_PAYMENT_METHOD,
APPLY_COUPON,
PLACE_ORDER
} from './graphql/mutations';
interface CheckoutFlowProps {
products: Product[];
onSuccess: (orderId: string) => void;
onError: (error: Error) => void;
}
export const CheckoutFlow: React.FC<CheckoutFlowProps> = ({
products,
onSuccess,
onError
}) => {
const [cartId, setCartId] = useState<string | null>(null);
const [step, setStep] = useState<number>(1);
const [shippingAddress, setShippingAddress] = useState<Address | null>(null);
const [paymentMethod, setPaymentMethod] = useState<string | null>(null);
// GraphQL mutations from Magento GraphQL Docs MCP examples
const [createCart] = useMutation(CREATE_EMPTY_CART);
const [addProducts] = useMutation(ADD_PRODUCTS_TO_CART);
const [setShipping] = useMutation(SET_SHIPPING_ADDRESS);
const [setPayment] = useMutation(SET_PAYMENT_METHOD);
const [applyCoupon] = useMutation(APPLY_COUPON);
const [placeOrder] = useMutation(PLACE_ORDER);
const handleCreateCart = async () => {
try {
const { data } = await createCart();
setCartId(data.createEmptyCart);
await handleAddProducts(data.createEmptyCart);
} catch (err) {
onError(new Error('Failed to create cart: ' + err.message));
}
};
const handleAddProducts = async (cartId: string) => {
try {
await addProducts({
variables: {
cartId,
cartItems: products.map(p => ({
sku: p.sku,
quantity: p.quantity
}))
}
});
setStep(2);
} catch (err) {
onError(new Error('Failed to add products: ' + err.message));
}
};
const handleSetShippingAddress = async (address: Address) => {
try {
await setShipping({
variables: {
cartId,
address: {
firstname: address.firstname,
lastname: address.lastname,
street: address.street,
city: address.city,
region: address.region,
postcode: address.postcode,
country_code: address.countryCode,
telephone: address.telephone
}
}
});
setShippingAddress(address);
setStep(3);
} catch (err) {
onError(new Error('Failed to set shipping address: ' + err.message));
}
};
const handlePlaceOrder = async () => {
try {
const { data } = await placeOrder({
variables: { cartId }
});
onSuccess(data.placeOrder.order.order_number);
} catch (err) {
onError(new Error('Failed to place order: ' + err.message));
}
};
// ... render checkout steps UI
};
Result: Production-ready checkout component with proper error handling, type safety, and following Magento best practices.
Phase 5: Testing & Validation
Agent generates tests:
describe('CheckoutFlow', () => {
it('should complete guest checkout successfully', async () => {
// Test cases generated from GraphQL examples
});
it('should handle inventory validation errors', async () => {
// Error scenarios from documentation
});
it('should apply discount codes correctly', async () => {
// Coupon examples from tutorials
});
});
Total Development Time: From requirements to tested, production-ready code: Under 5 minutes.
Benefits of MCP-Powered Agentic Development
1. Speed: 10-100x Faster Development
- No manual documentation browsing
- Instant API exploration
- Automated code generation
- Built-in best practices
2. Accuracy: Zero Hallucinations
- AI references real documentation
- Correct schema structures
- Valid parameter names
- Proper error handling
3. Completeness: Comprehensive Implementations
- AI explores related documentation
- Discovers edge cases
- Includes error handling
- Follows Magento conventions
4. Learning: Best Practices Built-In
- Uses official examples
- Implements recommended patterns
- Includes performance optimizations
- Proper security considerations
5. Scalability: Works for Any Magento Project
- Custom extensions
- Integrations
- Migrations
- Testing
- Documentation
Technical Implementation Guide: Getting Started Today
Prerequisites
System Requirements:
- Python 3.10 or higher
- Git
- 1 GB available disk space
- macOS, Linux, or Windows with WSL
For GraphQL MCP:
- Adobe Commerce documentation files (350+ markdown files)
For REST API MCP:
- Magento swagger.json file (included in package)
Step-by-Step Setup
Setting Up REST API MCP Server
1. Clone and Install
git clone https://github.com/florinel-chis/magento-api-mcp
cd magento-api-mcp
pip install -e .
2. Verify Installation
python3 tests/verify_parser.py
python3 tests/verify_db.py
python3 tests/verify_server.py
You should see:
✓ Parsed 594 endpoints
✓ Created database with FTS5 indexes
✓ All 5 MCP tools working
✓ Performance: <100ms searches
3. Configure MCP Client
For Claude Desktop, edit ~/Library/Application Support/Claude/claude_desktop_config.json:
{
"mcpServers": {
"magento-api": {
"command": "magento-api-mcp"
}
}
}
4. Restart Claude Desktop
The REST API tools are now available. Try: “Search for cart-related POST endpoints” and watch Claude use the search_endpoints tool.
Setting Up GraphQL Docs MCP Server
1. Clone Adobe Documentation
# This is the official Magento GraphQL documentation
git clone https://github.com/AdobeDocs/commerce-webapi.git
2. Clone and Install MCP Server
git clone https://github.com/florinel-chis/magento-graphql-docs-mcp
cd magento-graphql-docs-mcp
pip install -e .
3. Configure Documentation Path
Choose one method:
Method A: Environment Variable
export MAGENTO_GRAPHQL_DOCS_PATH="/absolute/path/to/commerce-webapi/src/pages/graphql"
echo 'export MAGENTO_GRAPHQL_DOCS_PATH="/path/to/docs"' >> ~/.zshrc
Method B: Symlink (Recommended)
ln -s /absolute/path/to/commerce-webapi/src/pages/graphql data
ls -la data/ # Verify symlink works
Method C: Sibling Directory
parent-directory/
├── magento-graphql-docs-mcp/
└── commerce-webapi/
└── src/pages/graphql/
Server auto-detects sibling directory.
4. Run Verification Tests
python3 tests/verify_parser.py
python3 tests/verify_db.py
python3 tests/verify_server.py
python3 tests/benchmark_performance.py
Expected output:
✓ Parsed 350 documents
✓ Extracted 963 code blocks
✓ Found 51 GraphQL elements
✓ All 8 MCP tools working
✓ Startup: 0.87s (cached)
✓ Search: 5.5ms average
5. Configure MCP Client
{
"mcpServers": {
"magento-graphql-docs": {
"command": "magento-graphql-docs-mcp",
"env": {
"MAGENTO_GRAPHQL_DOCS_PATH": "/absolute/path/to/commerce-webapi/src/pages/graphql"
}
}
}
}
Important: Use absolute paths in MCP configuration.
6. Try the Examples
cd examples
# Run product examples
python3 example_products.py
# Run customer examples
python3 example_customer.py
# Run cart/checkout examples
python3 example_cart_checkout.py
# Or run all
bash run_all_examples.sh
Running Both Servers Simultaneously
Configure both in Claude Desktop:
{
"mcpServers": {
"magento-api": {
"command": "magento-api-mcp"
},
"magento-graphql-docs": {
"command": "magento-graphql-docs-mcp",
"env": {
"MAGENTO_GRAPHQL_DOCS_PATH": "/path/to/commerce-webapi/src/pages/graphql"
}
}
}
}
Now Claude has access to all 13 tools (5 + 8) simultaneously!
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Issue: FileNotFoundError: Documentation directory not found
Solution:
# Verify path exists
echo $MAGENTO_GRAPHQL_DOCS_PATH
ls -la $MAGENTO_GRAPHQL_DOCS_PATH
# Check for .md files
ls $MAGENTO_GRAPHQL_DOCS_PATH/*.md
# If empty, check symlink
ls -la data/
# Re-clone if needed
git clone https://github.com/AdobeDocs/commerce-webapi.git
Issue: ModuleNotFoundError: No module named 'magento_graphql_docs_mcp'
Solution:
cd magento-graphql-docs-mcp
pip install -e .
Issue: Slow performance on first run
Solution: This is normal! First run parses all documentation (3-5 seconds). Subsequent runs use the cached database (0.87 seconds).
Issue: Database locked error
Solution:
# Remove database and recreate
rm ~/.mcp/magento-graphql-docs/database.db
rm ~/.mcp/magento-api/database.db
# Restart servers (will regenerate databases)
magento-graphql-docs-mcp
magento-api-mcp
Issue: MCP client shows “Server not found”
Solution:
- Test command directly:
which magento-graphql-docs-mcp - Use absolute paths in config
- Check logs:
~/Library/Logs/Claude/(macOS) - Verify environment variables are set
Performance & Scalability: Built for Speed
Real-World Benchmark Results
Both MCP servers have been extensively benchmarked on Apple Silicon (M1/M2) hardware. Here are the results:
REST API MCP Server:
| Operation | Performance | Comparison |
|---|---|---|
| Swagger parsing | 2-3 seconds | One-time cost |
| Database ingestion | 1-2 seconds | One-time cost |
| Endpoint search (594 endpoints) | <100ms | 5x faster than web scraping |
| Endpoint lookup | <50ms | 10x faster than API calls |
| Schema retrieval | <30ms | Instant |
| Database size | ~10 MB | Tiny footprint |
| Startup (cached) | 2-3 seconds | Near-instant |
GraphQL Docs MCP Server:
| Operation | Performance | Comparison |
|---|---|---|
| Doc parsing (350 files) | 2-3 seconds | One-time cost |
| Database ingestion | 1-2 seconds | One-time cost |
| Documentation search | 5.5ms average | 18x faster than 100ms target |
| Document retrieval | 8.2ms | Instant |
| GraphQL element search | 3.4ms | Ultra-fast |
| Direct FTS5 query | 0.7ms | Near-zero latency |
| Database size | ~30 MB | Includes 963 examples |
| Startup (cached) | 0.87 seconds | Fastest startup |
Performance Comparison: MCP vs Alternatives
| Approach | Startup Time | Search Time | Offline | Structured Data |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MCP Servers | 3-5s (first) / <1s (cached) | <10ms | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes |
| Web Scraping | 30-60 seconds | 200-500ms | ❌ No | ❌ No |
| Manual Docs | N/A | Manual browsing | ✅ Yes | ❌ No |
| Direct API Calls | 0 seconds | 500ms-2s | ❌ No | ✅ Yes |
| In-Memory Search | 10-30 seconds | 50-200ms | ✅ Yes | ⚠️ Partial |
Key Advantages:
- Cached Performance: After first run, both servers start in under 1 second
- Sub-10ms Searches: FTS5 indexes deliver Google-speed searches
- No Network Dependency: Work anywhere, even offline
- Consistent Performance: No variation based on network or API limits
- Minimal Resource Usage: SQLite databases fit in memory, minimal CPU
Scalability Considerations
Database Scalability:
- SQLite handles millions of rows efficiently
- FTS5 indexes scale logarithmically
- Current databases (~40 MB combined) easily fit in memory
- Tested with 10,000+ concurrent searches: no degradation
Multi-User Scenarios:
- Each developer runs their own MCP server instance
- No shared database contention
- No API rate limits or quotas
- Perfect for team environments
Large Documentation Sets:
- GraphQL server tested with 350+ documents: excellent performance
- REST server tested with 594+ endpoints: excellent performance
- Could scale to 10,000+ documents with same architecture
- FTS5 indexing strategy proven for large datasets
Update Frequency:
- File modification time checking prevents unnecessary re-parsing
- Full re-ingestion takes 3-5 seconds when needed
- Can be automated with filesystem watchers
- CI/CD integration possible for auto-updates
Advanced Use Cases: Beyond Basic Integration
Multi-API Strategy: REST + GraphQL
Modern Magento projects often use both REST and GraphQL APIs strategically:
REST API Best For:
- Admin panel integrations
- Backend automation
- Simple CRUD operations
- Existing REST clients
- Third-party integrations (ERP, PIM)
GraphQL Best For:
- Frontend applications (PWA, mobile)
- Complex queries with nested data
- Reducing over-fetching
- Real-time customer interactions
- Modern JavaScript frameworks
AI Agent Strategy with Both MCP Servers:
Agent analyzes requirement:
"Build inventory sync between ERP and Magento"
Agent decision process:
1. search_endpoints(queries=["inventory", "stock"]) via REST MCP
→ Finds POST /V1/inventory/source-items
2. search_documentation(queries=["inventory", "stock"]) via GraphQL MCP
→ Finds GraphQL queries for inventory display
3. Agent decides: Use REST for inventory updates (admin), GraphQL for frontend display
4. Agent generates hybrid solution:
- REST API client for ERP → Magento sync
- GraphQL queries for real-time stock display
- Shared TypeScript types from both schemas
Automated Testing: Documentation-Driven Test Generation
Use MCP servers to automatically generate comprehensive API test suites:
Workflow:
# Agent generates tests from documentation
agent_task = "Generate API tests for all cart endpoints"
# Step 1: Discover all cart endpoints (REST MCP)
endpoints = search_endpoints(queries=["cart"])
# Step 2: Get schema details for each
for endpoint in endpoints:
details = get_endpoint_details(endpoint.path, endpoint.method)
# Step 3: Find examples (GraphQL MCP)
examples = search_examples(query=endpoint.operation_id, language="json")
# Step 4: Generate tests
generate_test(
endpoint=details,
examples=examples,
test_framework="pytest"
)
Generated Test Example:
import pytest
import requests
class TestCartEndpoints:
base_url = "https://magento.test"
api_token = "your_token_here"
def test_create_empty_cart(self):
"""Test POST /V1/carts/mine - Create empty cart
Schema: quote-data-cart-interface
Status codes: 200 (Success), 401 (Unauthorized)
"""
response = requests.post(
f"{self.base_url}/rest/V1/carts/mine",
headers={"Authorization": f"Bearer {self.api_token}"}
)
assert response.status_code == 200
data = response.json()
assert "id" in data
assert isinstance(data["id"], int)
def test_add_product_to_cart(self):
"""Test POST /V1/carts/mine/items - Add product
Schema: quote-data-cart-item-interface
Status codes: 200 (Success), 400 (Bad Request), 404 (Not Found)
"""
# Test implementation from GraphQL examples
# ...
Code Migration: REST to GraphQL
Use both MCP servers to assist in migrating REST implementations to GraphQL:
Agent Workflow:
1. Analyze existing REST code
2. search_endpoints() to understand current REST endpoint
3. get_endpoint_details() to get response schema
4. search_graphql_elements() to find equivalent GraphQL query
5. get_element_details() to compare data structures
6. search_examples() to find working GraphQL implementation
7. Generate migration code with data mapping
Example Migration:
Before (REST):
// Old REST implementation
const response = await fetch('/rest/V1/products?searchCriteria[filter_groups][0][filters][0][field]=price&searchCriteria[filter_groups][0][filters][0][value]=50&searchCriteria[filter_groups][0][filters][0][condition_type]=gteq');
const products = await response.json();
After (GraphQL – Generated by AI):
query GetProducts($minPrice: Float!) {
products(
filter: {
price: { from: $minPrice }
}
) {
items {
id
sku
name
price_range {
minimum_price {
final_price {
value
currency
}
}
}
}
}
}
AI Agent Benefits:
- Identifies equivalent GraphQL queries
- Maps REST response fields to GraphQL fields
- Handles breaking changes
- Optimizes query structure
- Adds error handling
Documentation Generation: Create Custom Integration Guides
Use MCP servers to generate custom documentation for specific integration scenarios:
Agent task: "Create integration guide for B2B customer registration with custom attributes"
Agent process:
1. get_tutorial(tutorial_name="customer") via GraphQL MCP
2. search_graphql_elements(query="customer", element_type="mutation")
3. get_element_details(element_name="createCustomer")
4. search_endpoints(queries=["customer create"], filter_by_method="POST")
5. get_schema(name="customer-data-customer-interface")
6. search_examples(query="custom attributes")
Agent generates:
- Markdown documentation with working examples
- Code snippets in multiple languages
- API reference tables
- Step-by-step implementation guide
- Error handling documentation
Output: Custom Integration Guide
# B2B Customer Registration with Custom Attributes
## Overview
This guide demonstrates how to register B2B customers with custom attributes using both REST and GraphQL APIs.
## GraphQL Approach (Recommended)
### Step 1: Create Customer Account
\`\`\`graphql
mutation {
createCustomer(input: {
firstname: "John"
lastname: "Doe"
email: "[email protected]"
password: "SecurePass123"
custom_attributes: [
{ attribute_code: "company_name", value: "Acme Corp" }
{ attribute_code: "tax_vat", value: "GB123456789" }
]
}) {
customer {
id
email
firstname
lastname
}
}
}
\`\`\`
### Step 2: Add B2B Company Association
\`\`\`graphql
mutation {
assignCustomerToCompany(
customerId: 123
companyId: 456
) {
success
}
}
\`\`\`
## REST Approach
### POST /V1/customers
\`\`\`json
{
"customer": {
"email": "[email protected]",
"firstname": "John",
"lastname": "Doe",
"custom_attributes": [
{ "attribute_code": "company_name", "value": "Acme Corp" }
]
},
"password": "SecurePass123"
}
\`\`\`
...
Comparison with Traditional Approaches
MCP Servers vs Web Documentation
Traditional Web Documentation:
- ❌ Manual browsing and searching
- ❌ Copy-paste code snippets
- ❌ Human interpretation required
- ❌ Slow context switching
- ❌ Risk of outdated information
MCP Server Approach:
- ✅ Programmatic access for AI agents
- ✅ Instant search (<10ms)
- ✅ Structured, validated data
- ✅ Context preserved automatically
- ✅ Local, always consistent
MCP Servers vs API Testing Tools (Postman, Insomnia)
API Testing Tools:
- ⚠️ Manual collection creation
- ⚠️ Limited to REST (or limited GraphQL)
- ⚠️ No AI integration
- ⚠️ Requires manual updates
- ✅ Good for testing
MCP Servers:
- ✅ Automatic documentation parsing
- ✅ REST and GraphQL support
- ✅ Native AI integration
- ✅ Auto-updates from source
- ✅ Documentation + testing
Use Both: MCP servers for AI development, Postman/Insomnia for manual testing.
MCP Servers vs OpenAPI Generators
OpenAPI Code Generators:
- ✅ Generate client libraries
- ❌ REST only
- ❌ No documentation access
- ❌ No AI integration
- ❌ Boilerplate only
MCP Servers:
- ✅ AI generates custom code
- ✅ REST + GraphQL
- ✅ Full documentation access
- ✅ Native AI integration
- ✅ Production-ready implementations
Complementary: Use OpenAPI generators for base clients, MCP servers for AI-powered customization.
Future Roadmap & Community Involvement
Planned Features
REST API MCP Server:
Q2 2025:
- Multiple Magento version support (2.4.6, 2.4.7, 2.4.8)
- Deep
$refresolution for nested schemas - Request/response examples from OpenAPI
- Interactive schema explorer tool
- Custom swagger.json support for extensions
Q3 2025:
- Webhook documentation integration
- Admin API vs Store API differentiation
- Performance optimization for 1000+ endpoints
- Export to Postman collections
- GraphQL schema comparison tool
GraphQL Documentation MCP Server:
Q2 2025:
- Real-time documentation updates via GitHub Actions
- Custom tutorial support for third-party extensions
- Code generation templates (React, Vue, Angular)
- Multi-version documentation (2.4.6, 2.4.7, 2.4.8)
- Tutorial completion tracking
Q3 2025:
- Interactive query builder
- Video tutorial integration
- Community-contributed examples
- Translation support (multiple languages)
- Advanced search with semantic understanding
Join the Community
Both MCP servers are fully open-source and welcome contributions!
GitHub Repositories:
- REST API MCP: github.com/florinel-chis/magento-api-mcp
- GraphQL Docs MCP: github.com/florinel-chis/magento-graphql-docs-mcp
Ways to Contribute:
- Star the Repositories ⭐ – Show support and help others discover the tools
- Report Issues 🐛 – Found a bug? Documentation unclear? Let us know!
- Submit Pull Requests 💻 – Code improvements, new features, bug fixes
- Add Examples 📚 – Share your use cases and implementations
- Improve Documentation 📝 – Help others get started
- Share Your Experience 💬 – Blog posts, videos, tutorials
- Suggest Features 💡 – What would make these tools better?
Community Resources:
- GitHub Issues – Bug reports and feature requests
- GitHub Discussions – Questions and use cases
- Pull Requests – Code contributions welcome
- Examples Gallery – Community-contributed examples
Contributing Guidelines:
Both repositories include comprehensive CONTRIBUTING.md files with:
- Code style guidelines
- Testing requirements
- Pull request process
- Development setup instructions
Conclusion: The Future is AI-Powered, MCP-Enabled
We’re witnessing a fundamental shift in software development. AI agents augmented with tools like MCP servers aren’t just making development faster—they’re making it more accurate, more comprehensive, and more accessible.
Key Takeaways
1. MCP Bridges AI and Documentation
Model Context Protocol provides the missing link between AI agents and the vast documentation ecosystems that modern frameworks require. For Magento 2, this means AI agents can instantly access 594 REST endpoints and 350+ GraphQL documentation pages.
2. Two Servers, Complete Coverage
The REST API MCP Server delivers structured OpenAPI specifications perfect for API integration, while the GraphQL Documentation MCP Server provides narrative content, tutorials, and 963 working examples. Together, they cover every aspect of Magento API development.
3. Real Performance, Real Results
These aren’t prototype tools—they’re production-ready with benchmarked performance:
- REST API searches: <100ms across 594 endpoints
- GraphQL doc searches: 5.5ms average (18x faster than target)
- Startup time: <1 second (cached)
- Zero network dependency (fully offline)
4. Agentic Development Works Today
AI agents using these MCP servers can build production-ready Magento integrations in minutes. From custom checkout flows to complex B2B scenarios, the combination of instant documentation access and AI code generation transforms development speed.
5. Open Source, Community-Driven
Both servers are fully open-source, actively maintained, and welcoming contributors. This is just the beginning—the roadmap includes multi-version support, enhanced search, code generation templates, and community features.
Start Building Intelligent Magento Applications Today
The tools are ready. The documentation is waiting. The AI agents are capable. Now it’s your turn to experience the future of Magento development.
Get Started in 3 Steps:
- Clone the Repositories
# REST API MCP git clone https://github.com/florinel-chis/magento-api-mcp # GraphQL Docs MCP git clone https://github.com/florinel-chis/magento-graphql-docs-mcp - Install and Configure
cd magento-api-mcp && pip install -e . cd magento-graphql-docs-mcp && pip install -e . # Add to Claude Desktop config - Try an Example
# Run working examples cd magento-graphql-docs-mcp/examples python3 example_cart_checkout.py
Join the Community:
- ⭐ Star both repositories on GitHub
- 🚀 Try the servers with your next Magento project
- 💬 Share your experience and use cases
- 🤝 Contribute improvements and examples
- 📣 Help others discover these tools
The Promise of AI-Powered Development
These MCP servers represent more than just tools—they’re a glimpse into the future of software development. A future where:
- AI agents understand complex API ecosystems instantly
- Documentation is instantly accessible, not manually searched
- Code generation is accurate, complete, and production-ready
- Developers focus on architecture and business logic, not boilerplate
- Development speed is measured in minutes, not days
For Magento 2 specifically, this means:
- Build complex integrations in hours, not weeks
- Generate correct API implementations without trial and error
- Explore the complete API surface area instantly
- Learn best practices from official documentation
- Scale development with AI augmentation
Your Next Steps
For Magento Developers:
- Install both MCP servers today
- Try building your next integration with AI assistance
- Compare your speed with and without MCP servers
- Share your results with the community
For AI Engineers:
- Study how MCP protocol works
- Explore building custom MCP servers for other platforms
- Experiment with agentic development patterns
- Contribute to the open-source ecosystem
For Technical Leaders:
- Evaluate MCP servers for your team
- Measure productivity improvements
- Consider AI-powered development toolchains
- Plan your AI integration strategy
Resources & Links
Official Documentation
- Model Context Protocol – MCP specification and guides
- Anthropic Claude – AI assistant with native MCP support
- Magento DevDocs – Official Magento documentation
- FastMCP Framework – Python MCP server framework
MCP Server Repositories
Related Tools
- OpenAPI Specification – REST API spec format
- GraphQL – Query language for APIs
- SQLite FTS5 – Full-text search extension